
Two hydrogen bonds are formed between adenine and thymine, but three hydrogen bonds hold together guanine and cytosine (Figure 2.127). The double helix, made up of a pair of DNA strands, has at its core, bases joined by hydrogen bonds to form base pairs - adenine always paired with thymine, and guanine invariably paired with cytosine.

Today, every high school biology student is familiar with the double helical structure of DNA and knows that G pairs with C and A with T. Arguably, that one-page paper has had more scientific impact per word than any other research article ever published. Their famous paper, in the Apissue of Nature, opened the modern era of molecular biology. X-ray diffraction work of Rosalind Franklin and the observations of Erwin Chargaff were combined by James Watson and Francis Crick to form a model of DNA that we are familiar with today. Discovered in 1869 by Friedrich Miescher, DNA was identified as the genetic material in experiments in the 1940s led by Oswald Avery, Colin MacLeod, and Maclyn McCarty. The race to elucidate the structure of DNA was one of the greatest stories of 20th century science. We will begin with DNA, which is the hereditary information in every cell, that is copied and passed on from generation to generation. In this section, we will examine the structures of DNA and RNA, and how these structures are related to the functions these molecules perform. The nucleic acids, DNA and RNA, may be thought of as the information molecules of the cell.
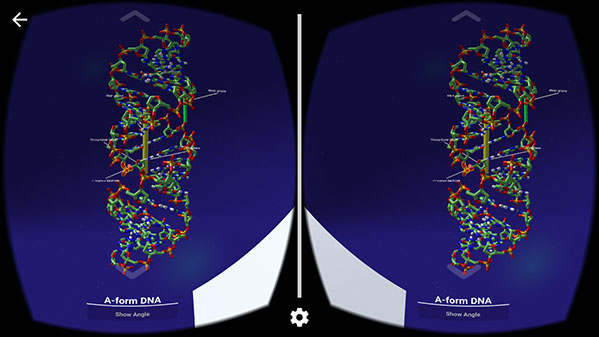
A FORM B FORM Z FORM C FORM OF DNA FOR FREE
The entire textbook is available for free from the authors at


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
